An assessment team typically comprises 3 or 4 trained assessors (could be more), one of whom is the designated team leader. These independent TADAT trained assessors are responsible for determining the TADAT assessment ratings using evidence. The team may also include some analysts in a supporting role to assist in data collection, evidence gathering, and analysis.
198
Total Assessments
149
National Assessments
49
Subnational Assessments
160
First Assessments
38
Repeat Assessments
The Tool:
There are 9 key performance outcome areas (POAs) covering most critical tax administration functions, processes and institutions. They are assessed on 32 high-level indicators, each built on 1 to 5 dimensions adding up to 55 measurement dimensions, making TADAT a comprehensive but administrable diagnostic tool.
TADAT focuses on the performance of the major national taxes: Corporate Income Tax (CIT), Personal Income Tax (PIT), Value Added Tax (VAT) (or its indirect tax equivalent such as sales tax), and Pay As You Earn (PAYE) amounts withheld by employers (which, strictly speaking, are remittances of PIT). Social Security Contributions (SSCs) may also be included in assessments where SSCs are a major source of government revenue and are collected by the tax administration, as is the case in many European countries.
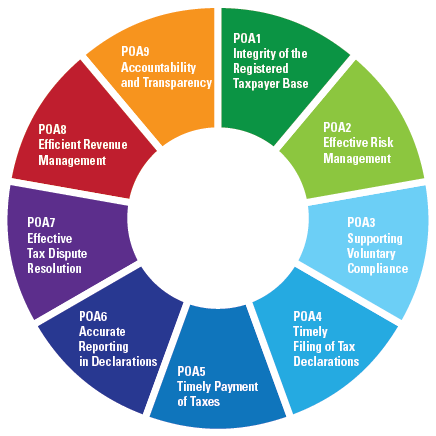
Performance Outcome Areas
Integrity of the Registered Taxpayer Base
All businesses, individuals, and other entities that are required to register are included in a taxpayer registration database. Information held in the database is complete, accurate, and up-to-date.
Indicator
Integrity of the Registered Taxpayer Base
All businesses, individuals, and other entities that are required to register are included in a taxpayer registration database. Information held in the database is complete, accurate, and up-to-date.
Knowledge of the potential taxpayer base
The extent of initiatives to detect businesses and individuals who are required to register but fail to do so.
Effective Risk Management
Risks to revenue and tax administration operations are identified and managed effectively.
Indicator
Identification, assessment, ranking and quantification of compliance risks
Extent of intelligence gathering and research to identify compliance risks in respect of the main tax obligations.
Process used to assess, rank, and quantify taxpayer compliance risks.
Mitigation of risks through a compliance improvement plan
Degree to which the tax administration mitigates assessed risks to the tax system through a compliance improvement plan.
Monitoring and evaluation of compliance risk mitigation activities
Process used to monitor and evaluate the impact of compliance risk mitigation activities.
Management of operational risks
The process used to identify, assess and mitigate operational risks.
The extent to which the effectiveness of the business continuity program is tested, monitored and evaluated.
Supporting Voluntary Compliance
Taxpayers have the necessary information and support to voluntarily comply at a reasonable cost to themselves.
Indicator
Scope, currency and accessibility of information
The range of information available to taxpayers to explain, in clear terms, their obligations and entitlements for each core tax.
The degree to which information is current in terms of the law and administrative policy.
The availability to taxpayers of information and guidance from the tax administration.
The time taken to respond to information requests.
The time taken to respond to taxpayers and tax intermediaries’ requests for information.
Scope of initiatives to reduce taxpayer compliance costs
The extent of initiatives to reduce taxpayer compliance costs.
Obtaining taxpayer feedback on products and services
The use and frequency of methods to obtain feedback from taxpayers on the standard of services provided.
The extent to which taxpayer input is taken into account in the design of administrative processes and products.
Timely Filing of Tax Declarations
Taxpayers file tax declarations on time.
Indicator
On -time filing rate
The number of CIT declarations filed by the statutory due date as a percentage of the number of declarations expected from registered CIT taxpayers.
The number of PIT declarations filed by the statutory due date as a percentage of the number of declarations expected from registered PIT taxpayers.
The number of VAT declarations filed by the statutory due date as a percentage of the number of declarations expected from registered VAT taxpayers.
Management of non-filers
Action taken to follow up on non-filers.
Use of electronic filing facilities
The extent to which tax declarations are filed electronically.
Timely Payment of Taxes
Taxpayers pay their taxes in full on time.
Indicator
Use of electronic payment methods
The extent to which core taxes are paid electronically.
Use of efficient collection systems
The extent to which withholding at source and advance payment systems are used.
Timeliness of payments
The number of VAT payments made by the statutory due date in percent of the total number of payments due.
The value of VAT payments made by the statutory due date in percent of the total value of VAT payments due.
Stock and flow of tax arrears
The value of total core tax arrears at fiscal year-end in percent of total core tax revenue collections for the fiscal year.
The value of collectible core tax arrears at fiscal year-end in percent of total core tax revenue collections for the fiscal year.
The value of core tax arrears more than 12 months’ old in percent of the value of all core tax arrears.
Accurate Reporting in DeclarationsAccurate Reporting in Declarations
Taxpayers report complete and accurate information in their tax declarations.
Indicator
Scope of verification actions taken to detect and deter inaccurate reporting.
The nature and scope of the tax audit program in place to detect and deter inaccurate reporting.
The extent to which the audit program is systematized around uniform practices.
Use of large-scale data-matching systems to detect inaccurate reporting
The extent of large-scale automated crosschecking to verify information reported in tax declarations.
Initiatives undertaken to encourage accurate reporting
The nature and scope of proactive initiatives undertaken to encourage accurate reporting.
Effective Tax Dispute Resolution
The tax dispute resolution process is fair and independent, accessible to taxpayers, and effective in resolving disputed matters in a timely manner.
Indicator
Existence of an independent, workable, and graduated dispute resolution process
The extent to which an appropriately graduated mechanism of administrative and judicial review is available to, and used by, taxpayers.
Whether the administrative review mechanism is independent of the audit process.
Whether information on the dispute process is published, and whether taxpayers are explicitly made aware of it.
Time taken to resolve disputes
The time taken to complete administrative reviews.
Efficient Revenue Management
Tax revenue collections are fully accounted for, monitored against expectations, and analyzed to inform government revenue forecasting. Legitimate tax refunds are paid promptly.
Indicator
Contribution to government tax revenue forecasting process
The extent of tax administration input to government tax revenue forecasting and estimating.
Adequacy of the tax revenue accounting system
Adequacy of the tax administration’s tax revenue accounting system.
Adequacy of tax refund processing
Adequacy of the VAT refund system.
The time taken to pay (or offset) VAT refunds.
Accountability and Transparency
The tax administration is transparent in the conduct of its activities and accountable to the government and community.
Indicator
Internal assurance mechanisms
Assurance provided by internal audit.
Staff integrity assurance mechanisms.
Public perception of integrity
The mechanism for monitoring public confidence in the tax administration
Publication of activities, results, and plans
The extent to which the financial and operational performance of the tax administration is made public, and the timeliness of publication.
The extent to which the tax administration’s future directions and plans are made public, and the timeliness of publication.
Upcoming Events
Latest News
Check out USAID's Collecting Taxes Database (CTD) here .
New Virtual Training to Advance Revenue Administration (VITARA), to register please click here .
Read about TADAT in Volume 2 of the Belt and Road Initiative Tax Journal here .
New TADAT Insights Paper on POA1 and the integrity of the registered taxpayer base available in English, Spanish, French, Portuguese.
For more on TADAT, visit and subscribe to the TADAT YouTube Channel here.
The TADAT Secretariat released a revised online training course based on the 2019 Field Guide. Now also available in Spanish. You can apply here.
- The Assessment
- Assessment Process
- Assessment Teams
A TADAT assessment provides a baseline that informs country authorities on areas in need of improvement so that they can prioritize, plan and sequence responses/interventions
The TADAT assessments:
- Identify the relative strengths and weaknesses in systems, processes, and institutions.
- Create a shared view on the condition of the system among all stakeholders (e.g., country authorities, international organizations, donor countries, and technical assistance providers).
- Set the reform agenda, including reform objectives, priorities, initiatives, and implementation sequencing.
- Facilitate coordination of external support for reforms and achieving more efficient implementation.
- Monitor and Evaluate reform progress by way of subsequent repeat assessments.
Phase 1. Assessment initiation
The client country sends a formal request either to a sponsor or the TADAT secretariat directly.
Phase 2. Pre-assessment
This is the assessment team’s planning and preparation phase that begins 6 to 8 weeks prior to the in-country assessment phase.
Phase 3. In-country assessment
The assessment team, together with the country’s officials, uses the TADAT methodology to assess the health status of the country’s system of tax administration using concrete evidence and field office visits, and document the results in a Performance Assessment Report (PAR).
Phase 4. Post-assessment
The PAR is finalized during this phase in which the team leader incorporates the authorities’ comments and sends, for final review and certification, the revised PAR to the TADAT Secretariat, who then publish the results on the TADAT Website unless the country chooses to opt-out.